Which of the Following Circumstances Creates a Future Taxable Amount
Higher tax rates in the future compared to the past. A deferred tax asset is an item on a companys balance sheet that reduces its taxable income in the future.
Enter any net advances on line 17 under the same column as the open account debt.

. Accrued compensation costs for future payments. In settling the liability for its carrying amount the entity will reduce its future taxable profit by an amount of 100 and consequently reduce its future tax payments by 25 100 at 25. Such a line item asset can be found when a business overpays its taxes.
Answers a and b are temporary differences that would result in future. Paragraph IAS 1235 specifically emphasises that the existence of unused tax losses is strong evidence that future taxable profit may not be available and that an entity with a history of recent losses recognises a deferred tax asset arising from unused tax losses or tax credits only to the extent that the entity has sufficient taxable temporary differences or there is. The difference between the carrying amount of 100 and the tax base of nil is a deductible temporary difference of 100.
Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation for tax reporting. Single taxpayers reach the phase-in range once taxable income exceeds 160700 and enter the upper threshold at 210700. An increase in a deferred tax asset.
Deferred tax liabilities are the amounts of income taxes payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences. Promoting shares in an audit client. Which of the following circumstances creates a future taxable amount.
Lets say that a business incurs a loss on the sale of an asset. The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 increased the maximum amount that can be excluded from an employees income through a dependent care assistance program. Deferred tax assets are the amounts of income taxes recoverable in future periods in respect of deductible temporary differences carry forward of unused tax losses and carry forward of unused tax credits.
Premiums on officers life insurance. Which of the following items results in a temporary difference taxable amount for a given year. Which of the following circumstances creates a future taxable amount.
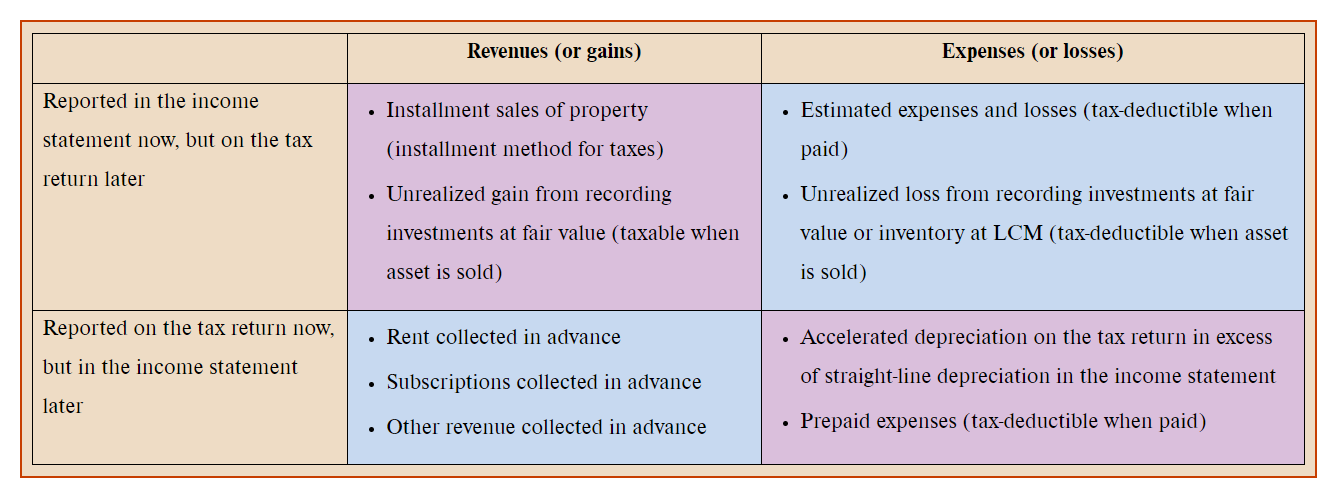
Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation for tax reporting. Conversely if the revenue is recognised for tax purposes when the goods or services are received the tax base will be equal its carrying amount. Taxable when received recognized for financial reporting when earned.
Accrued compensation costs for future payments. Which of the following circumstances creates a future taxable amount. For 2021 the amount is increased to 10500 previously 5000.
For married filing separate returns the amount is increased to 5250 previously 2500. Taxable when received recognized for financial reporting when earned. It refers to a situation where the.
If you dont receive your Form 1099-G by mid-February you may call. If there are no tax consequences from repayment of. Which of the following creates a permanent difference between financial income and taxable income.
One results in a future taxable amount such as revenue earned for financial accounting purposes but deferred for tax accounting purposes. If the firm can recognize the loss on a future tax return the loss is a deferred tax asset. Which of the following circumstances creates a future taxable amount.
Will exceed future financial accounting income. See Regulations section 11367-2d2. The following circumstances create advocacy threats for a professional accountant in public practice except A.
Service fees collected in advance from customers. Married Filing Jointly taxpayers reach the phase-in threshold when taxable income exceeds 321400 and enter the upper threshold at 421400. In order to determine taxable income each January the EDD sends a Form 1099-G to each individual for the total unemployment insurance benefits paid during the prior year.
Acting as an advocate on behalf of an audit client in litigation or disputes with third parties. Consider the following example for deferred tax assets. For tax purposes faster than it was depreciated for financial.
Accrued compensation costs for future payments. The deferred tax assets refers to the assets that helps in reducing taxable income of the company and help in reducing the tax that is to be paid by the company. This money will.
If the revenue is taxed on receipt but deferred for accounting purposes the tax base of the liability is equal to equal to nil as there are no future taxable amounts. Interest received on municipal bonds. Which of the following circumstances creates a future taxable amount.
A deferred tax asset refers to the asset that is shown on the balance sheet of the company on the asset side. Accounting depreciation meaning future taxable income. Taxable when received recognized for.
When the Penalty Kicks In. Service fees collected in advance from customers. Typically an underpayment penalty may apply if the amount withheld or paid through estimated taxes is not equal to the smaller of 90 of the taxes you owe for the.
Service fees collected in advance from customers. This may happen if a company uses the cash method for tax preparation. Service fees collected in advance from customers.
For corporations deferred tax liabilities are netted against deferred tax assets and reported on the balance sheet. Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation for tax reporting Which of the following usually results in an increase in a deferred tax liability. See the details of.
Taxable when received recognized for financial reporting when earned. The second type of temporary difference is a future deductible amount. Advances and repayments made during the S corporations tax year on an open account are netted at the close of the S corporations tax year to determine the amount of any net advance or net repayment.
In future years tax depreciation will be less than financial. Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation for tax reporting.

Ch19 Kieso Intermediate Accounting Solution Manual

Ch19 Kieso Intermediate Accounting Solution Manual
Chapter 16 Flashcards Chegg Com

Ch19 Kieso Intermediate Accounting Solution Manual

Ch19 Kieso Intermediate Accounting Solution Manual

Ch19 Kieso Intermediate Accounting Solution Manual
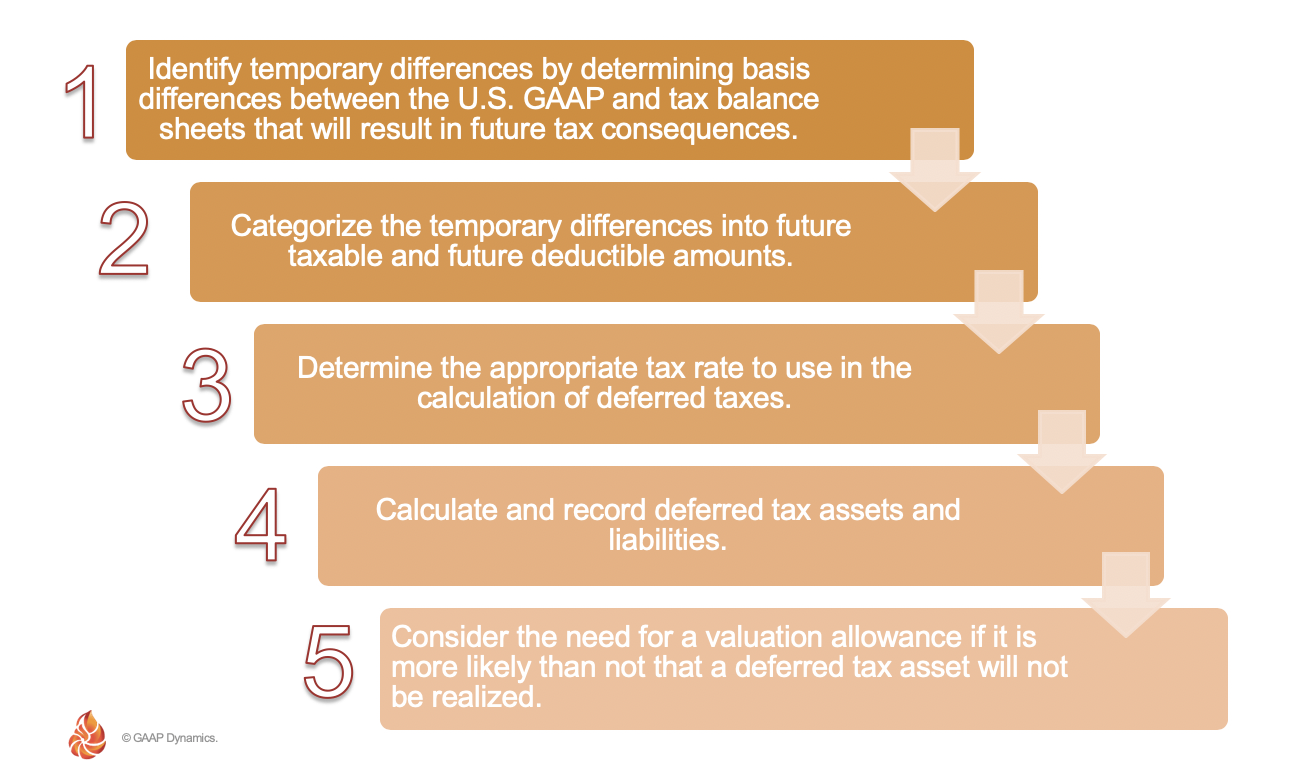
Accounting For Income Taxes Under Asc 740 Deferred Taxes Gaap Dynamics

What Are Deferred Tax Assets And Deferred Tax Liabilities Article

Ch19 Kieso Intermediate Accounting Solution Manual

Solved Using Straight Line Depreciation For Financial Chegg Com
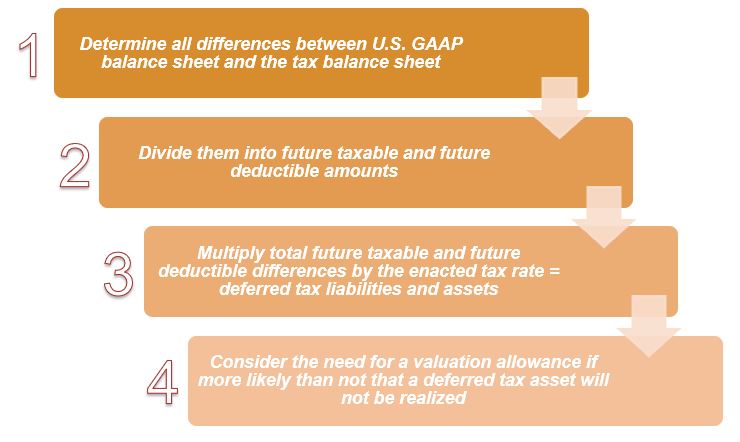
/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment